If you are an active person, knee niggles can be common and something you live with. Often, easing off a little seems to solve the problem. But what happens when things don’t seem to get better by themselves, and the pain continues? You could be suffering from patellar tendonitis, or jumper’s knee.
What is patellar tendonitis?
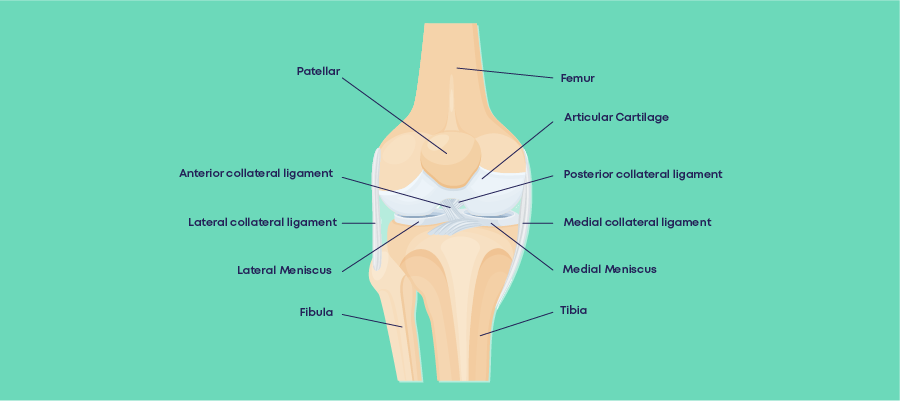
Patellar tendonitis is a fairly common soft tissue injury. It affects the patellar tendon at the front of your knee, below the kneecap. This tendon connects the kneecap (patella) to the shin bone (tibia). Patellar tendonitis weakens the tendon, which if untreated, can lead to tearing.
What causes patellar tendonitis?
The specific cause of patellar tendonitis is not fully understood, but it is linked to the overuse of the knee joint. It is a common injury in people who participate in jumping and running activities, such as volleyball, tennis, football, and badminton. In high level volleyball alone, more than 40% of players suffer from knee overuse injuries.
Overuse of the knee means that over time, the tendon is unable to adapt to the level of strain put on it, leading to micro tears of the tendon fibres. As the tendon attempts to heal, it will thicken, which can lead to pain and irritation. Contributing factors to patellar tendonitis also include uneven muscle strength, misaligned feet, ankles and legs, obesity, and playing sport on hard surfaces.
What are the symptoms of patellar tendonitis?
The first symptom of patellar tendonitis is often pain or tenderness at the base of your kneecap, making it very tender to touch or squeeze. People often notice stiffness around the tendon when they first get up in the morning, or walk downstairs. The pain may be sporadic, occurring only after sports or physical activity. As the tendon becomes more damaged, the pain can become progressively worse. It can start to interfere with daily activities, such as climbing stairs or driving a car.
What is the best treatment for tendonitis of the knee?
The first stage of treatment of moderate or severe patellar tendonitis is to get it diagnosed correctly, to check for complications and assess the underlying causes. This can be done by a GP or qualified osteopath.
Ice can be used to reduce swelling. An ice pack, or bag of frozen peas, wrapped in a damp tea towel can be applied to the knee for a maximum of 20 minutes, up to 4 times a day.
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen, can be used for a few days, always ensuring they are taken with food.
Rest, or at least reduced knee activity, is highly recommended to give the tendon time to heal. Alternative low-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling, can help maintain fitness levels.
Strengthening and stretching of the supporting muscle groups, including glutes, hamstring, quads, and calves, can help reduce the risk of recurrence. A qualified osteopath will be able to assess the injury, and create a unique set of exercises to aid recovery.
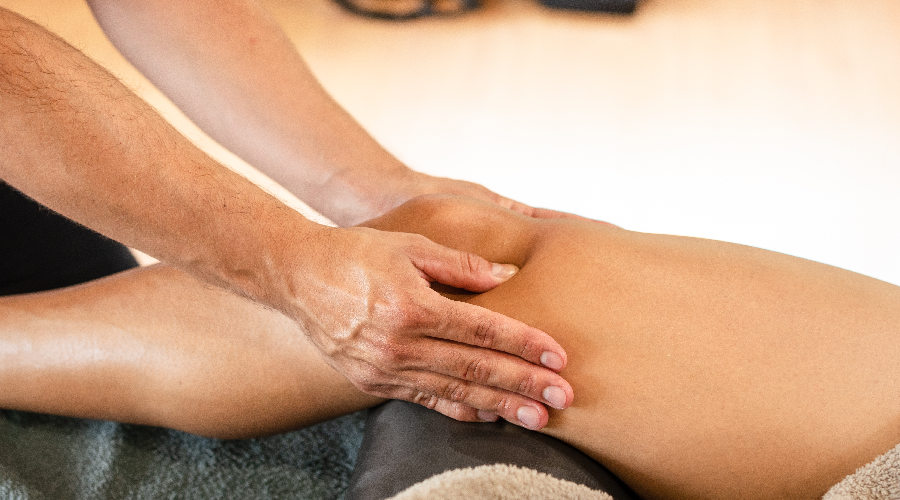

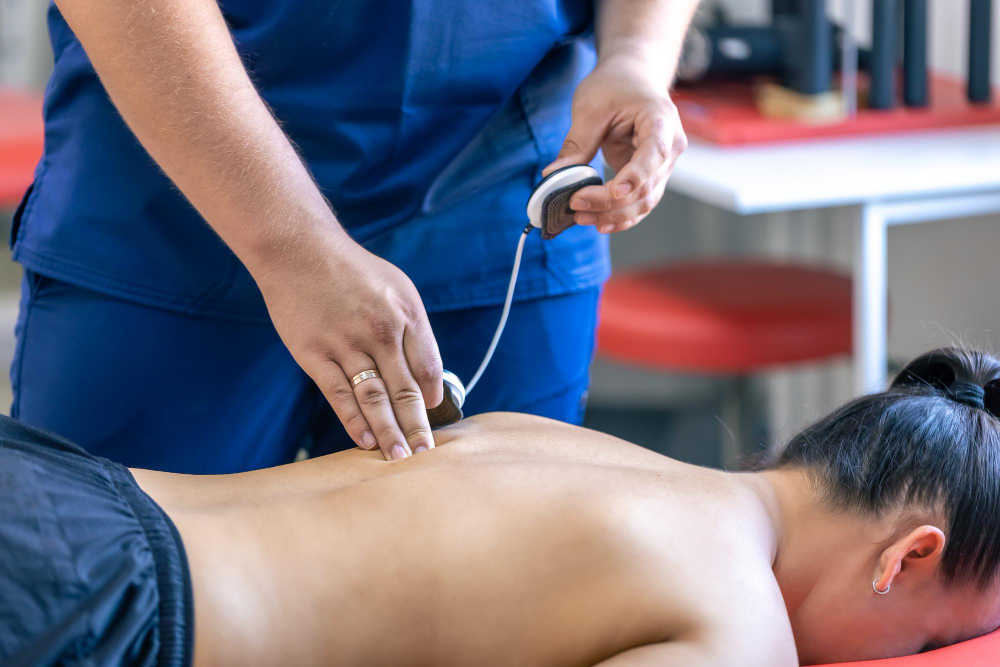
Knee pain Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive treatment performed with a hand-held device that creates high-energy pressure waves, transmitted to the injured tissue to provide pain relief. It initiates an inflammation-like condition in the tissue that is being treated, and the body responds by increasing the blood circulation and metabolism in the area. This in turn accelerates the body’s own healing process and stimulates cell regeneration.
Shockwave treatment is highly effective for treating patellar tendonitis. In a 2012 study, 33 patients with chronic patellar tendinopathy received low-energy ESWT, whilst a similar sized control group received other forms of therapy. The study concluded that:
“ESWT is an effective treatment for chronic patellar tendinopathy.”
These results are inline with other studies, which have shown ESWT to be:
“Efficacious and safe for reducing pain and improving knee function in patients with knee osteoarthritis, without increasing the risk of adverse effects.”
How can Carl Todd Clinics help?
Carl Todd Clinics have a wealth of experience in treating knee injuries, including patellar tendonitis. Our qualified osteopath and Shockwave therapists are on hand to help you recover from your injury in the shortest possible time, enabling you to get back to the sports and activities you love.